Noble metal thermocouple has the advantages of high temperature measurement accuracy, good stability, wide temperature measurement range, and long life. They are widely used in iron and steel, metallurgy, petrochemical, glass fiber, electronics, aviation and aerospace and other fields. However, the strength of Noble metal thermocouple decreases in high temperature environments, and they are sensitive to environmental pollution. It is difficult to adapt to complex environments where bending and short thermal response time are required in narrow spaces.
Noble metal Mineral insulated thermocouple is a new type of temperature measuring material developed on the basis of Noble metal assembly thermocouple. The magnesia or other insulating materials, and the pair wire and insulating material are assembled in a precious metal alloy tube and drawn repeatedly. And annealing treatment, processed into a slender non-detachable solid body, which has the advantages of vibration resistance, high pressure resistance, medium chemical corrosion resistance, bending ability, short response time and durability.
1. Structure &Advantages
(1) . Structure
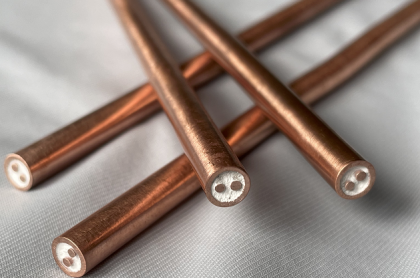
Noble metal MI thermocouple is mainly composed of precious metal casing, insulating material, and even wire material. Usually, magnesia or other insulating materials are filled between the noble metal outer casing and the even wire, so that the even wire is airtight while maintaining high temperature insulation. state, thereby preventing the thermocouple wire from corroding and deteriorating due to air or gas at high temperature. The hot end of the noble metal MI thermocouple can be made into grounded type, insulated type, exposed type, and the type with a block chamber for measuring the temperature of high-speed transient airflow, as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1
A. Grounded type; B. Insulated type; C. Exposed type; D. Blocked type
(2) .Advantages
A. Corrosion resistance, due to the protection of the metal tube, the noble metal MI thermocouple wire is protected by air tightness, and can be used even in oxidizing and corrosive environments;
B. Good stability of thermoelectric, and the thermoelectric drift is small for long-term use;
C. The operating temperature is high up to 1500C;
D. The end of the MI thermocouple is airtightly sealed, and there is no residual gas inside, and the thermocouple wire is not easy to deteriorate due to chemical reactions;
E. High insulation resistance, noble metal MI thermocouple can reach more than 50 MΩ at room temperature;
F. Specifications and tube materials can be processed according to requirements, suitable for various environments and durable;
G. Easy to bend, good flexibility, easy to install and assemble, and the installation conditions are not harsh;
H. Pressure and vibration resistance;
I. Short thermal response time;
J. Long life, because of the protection of the outer metal tube, the service life of the thermocouple is longer.
2. Sheath
The sheath material of noble metal MI thermocouple is usually composed of platinum, platinum alloy or iridium, iridium-rhodium alloy. Platinum and platinum alloy have the following characteristics:
(1) . High melting point;
(2) .High oxidation resistance and thermal stability in the atmosphere above 900 °C;
(3) .High corrosion resistance, ability to withstand HNO3 , HCN, HF and severe corrosion of molten glass and other silicate melts up to 1600°C;
(4) .High temperature strength and mechanical stability;
(5) .Good ductility and machinability, can be made into required structural parts and products;
(6) .Good weld ability, the required components can be prepared by welding.
Pure platinum has low strength at high temperature and is often damaged by its own weight and high-temperature impact and vibration. Therefore, rhodium is added to platinum to improve the high-temperature strength and high-temperature impact capability of the material.Generally, platinum-rhodium alloy with low rhodium content can be used up to 1500°C in the atmosphere, and platinum-rhodium alloy with a mass fraction of Rh greater than 20% can be used up to 1700°C in the atmosphere.
3. Wire
Noble metal MI thermocouple wire is mainly divided into two categories: standard Pt/PtRh thermocouple wire and non-standard thermocouple wire.
There are 3 types of standard thermocouple: Type S (Pt/PtRh10), Type R (Pt/PtRh13) and Type B (PtRh6/PtRh30).
The S-type thermocouple is composed of pure platinum wire as the negative leg and PtRh10 alloy wire as the positive leg. It can be used in an oxidizing atmosphere, vacuum and neutral atmosphere for a long time up to 1300 ° C, and for a short time up to 1600 ° C, which is the most widely used thermocouple in the temperature range of 1000~1300° C; the R-type thermocouple is composed of pure platinum wire as the negative leg and PtRh13 alloy wire as the positive leg. The electromotive force output of the R-type thermocouple is slightly higher than that of the S-type thermocouple. Its sensitivity and measurement range are the same as those of S-type; B-type thermocouple is composed of PtRh6 alloy wire as the negative electrode and PtRh30 alloy wire as the positive electrode. The sensitivity of the couple is the same as that of the S-type and R-type thermocouple, and the B-type thermocouple is mainly used for temperature measurement above 1400°C and are available for a short period of time to 1800°C, the temperature error is 3°C. Standard precious metal thermocouple is recommended because of their good thermal stability and plastic processing performance.
Non-standard thermocouple wire mainly include PtRh5/PtRh20, PtRh20/PtRh40, thermocouple composed of platinum alloy/gold alloy or palladium alloy, and IrRh alloy thermocouple, etc. Most non-standard thermocouple is used in some special occasions such as measuring gas turbine temperature, nuclear field temperature measurement, etc.
4. Insulated Material
The insulation resistance of noble metal MI thermocouple is directly related to the insulating material. The purity, shape (powder or tube) and thickness of the insulating layer of the insulating material will all affect the insulation resistance. The commonly used insulating materials are powdered ceramic oxides such as alumina, magnesia, zirconia, beryllia, thorium oxide, etc. As you can see in Table 1.
Among these insulating materials, magnesia has good compatibility and and low cost, which is the preferred insulating material for noble metal MI thermocouple products. However, it is easy to absorb moisture, which makes it sensitive to pollution such as oil gas, moisture in the air, sweat and fluff. After being polluted, the insulation resistance will decrease, so necessary precautions should be taken during processing. The insulation performance of zirconia decreases at high temperature, and it is unstable in medium containing halogen, sulfur and carbon at high temperature. When the temperature is higher than 1900°C, beryllia will decompose in hydrogen or other reducing media. It will decompose at a temperature of 1800°C and in the hydrogen-containing medium, and produce poisonous gas when the temperature is higher than 2200°C; thoria is radioactive when the temperature is 1600~2200°C. So zirconia, beryllia, and thoria are not suitable for noble metal MI thermoelectrics Even insulating material.
|
Insulated Material
|
Compound properties
|
Minimum purity/%
|
Melting point/°C
|
Refractoriness
|
Operating temperature
|
Average expansion coefficient (25~700°C)/10-6
|
|
MgO
|
alkaline
|
99.4
|
2800
|
2400
|
1650
|
12.9
|
|
Al2O3
|
neutral
|
99.5
|
2010
|
1950
|
1540
|
7.1~8.0
|
|
ZrO2
|
acidic
|
99.4
|
2680
|
2500
|
1650
|
4.2~5.2
|
|
BeO
|
alkaline
|
99.8
|
2510
|
2400
|
2310
|
8.1
|
|
ThO2
|
alkaline
|
99.5
|
3288
|
2700
|
2500
|
12.9
|
Table 1
5. Application
Noble metal MI thermocouple is widely used in vacuum furnaces in the iron and steel metallurgy industry, cracking furnaces in the petrochemical industry, and nuclear reactor fuels in the atomic energy industry due to their advantages such as accurate temperature measurement, good stability, corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, flexibility, and long life. It has been applied in fields such as component cladding temperature measurement. Get more details from www.super-instrument.com.










 IPv6 network supported
IPv6 network supported